The Legal Landscape of Cannabis in the United States: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the legal status of cannabis in the United States has become increasingly complex due to cannabis laws that differ dramatically from one state to another. As of 2024, the landscape continues to evolve, with more states adopting varying degrees of legalization and regulation. This guide provides a detailed overview of the current cannabis legalization landscape across the country.

Categories of Cannabis Legalization
- Recreational Cannabis Use:
Several states, including California, Colorado, and Oregon, have fully legalized cannabis for recreational use. Adults in these states can legally purchase and consume cannabis products like flowers, edibles, and concentrates through state-regulated dispensaries. These dispensaries operate under strict cannabis regulations to ensure product safety and compliance with state laws.
- Medical Marijuana:
Medical marijuana is legal in many states, allowing patients access to cannabis for specific health conditions. States like Arizona and Florida have well-established programs requiring patients to obtain a medical marijuana card, typically issued upon a doctor’s recommendation for conditions such as chronic pain, epilepsy, or multiple sclerosis. The qualifying conditions and process for obtaining a medical marijuana card vary significantly between states.
- Cannabis Decriminalization:
To reduce the burden on the criminal justice system, some states have decriminalized cannabis, where possession of small amounts is no longer a criminal offense. Instead, individuals caught with small quantities face civil fines or citations rather than criminal charges. Decriminalization aims to mitigate the long-term consequences of cannabis-related arrests, such as difficulties with employment and housing.
- High CBD/Low THC Cannabis Products:
Certain states permit the use of cannabis products high in CBD and low in THC, often for medical purposes. These products are particularly prescribed for conditions like epilepsy, where CBD has shown efficacy in reducing seizures. Regulations surrounding these products differ by state; some require a prescription, while others allow over-the-counter sales.
- Complete Cannabis Prohibition:
Despite growing acceptance nationwide, a few states still enforce strict anti-cannabis laws. In these jurisdictions, possession, sale, and use of cannabis are illegal, and violations are met with severe penalties. These states reflect local political and social resistance to cannabis legalization.
State-by-State Differences in Cannabis Regulations
- Cannabis Regulatory Frameworks:
Each state with legalized cannabis has developed its own regulatory framework, dictating how cannabis can be cultivated, sold, and consumed. These frameworks include licensing requirements for dispensaries, cultivation centers, and testing laboratories. In states with legal markets, rigorous testing and labeling are mandated to ensure product safety and transparency regarding THC and CBD content.
- Medical Marijuana Certification:
The process for obtaining medical marijuana varies significantly across states. Some states have extensive lists of qualifying conditions and require detailed documentation from healthcare providers, while others have more restrictive processes. Additionally, obtaining a medical marijuana card differs, with some states offering online registration and others requiring in-person appointments.
- CBD Products:
The legality of CBD products is a gray area with laws differing from state to state. Although the 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp-derived CBD at the federal level, some states impose restrictions on its sale and use. In certain states, CBD products are readily available in mainstream retail stores, while others limit sales to licensed dispensaries.
The Federal Impact on Cannabis Law
Although a growing number of states have legalized cannabis in some form, it remains illegal under federal law. This federal prohibition creates challenges for cannabis businesses, particularly in banking, where access to traditional financial services is limited. Additionally, federal restrictions hinder scientific research on cannabis due to its classification as a Schedule I drug under the Controlled Substances Act. However, momentum for federal reform is building, with various bills introduced in Congress aimed at decriminalizing or legalizing cannabis nationwide.
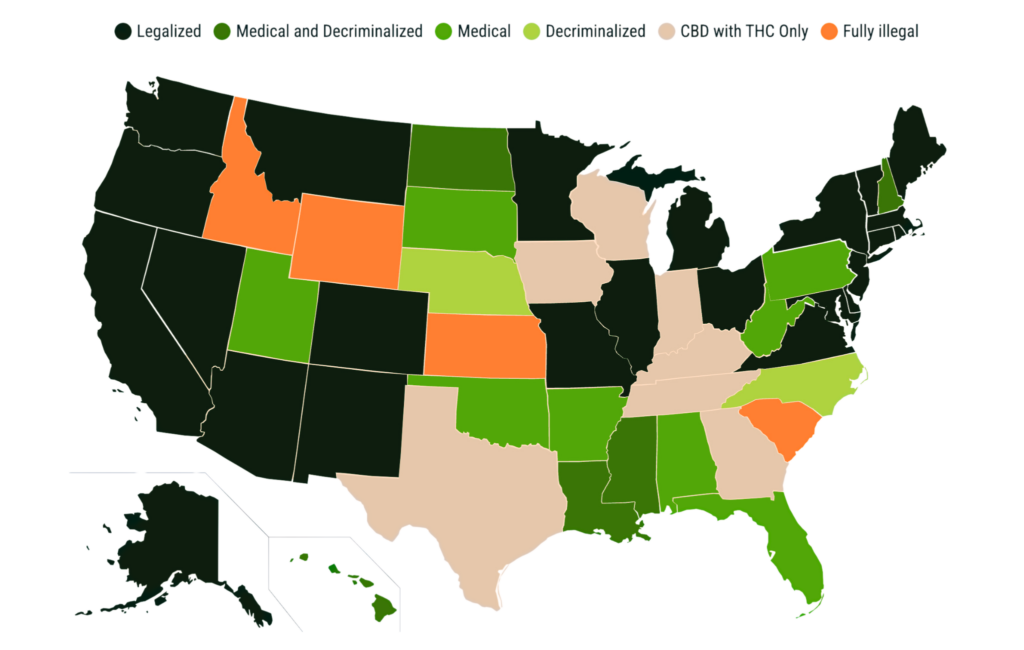
Maps Showing the Legal Status of Cannabis Across the United States in 2024
- Recreational Cannabis:
As of April 2024, recreational marijuana is legal in 24 states, including Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Rhode Island, Vermont, Virginia, and Washington, D.C. Adults aged 21 and older can purchase and consume cannabis in these states.
- Medical Marijuana:
Medical marijuana is legal in 13 states beyond those allowing recreational use. States like Alabama, Arkansas, and Florida permit medical marijuana but not recreational use. Decriminalization measures in some states reduce penalties for non-medical cannabis possession, while other states remain more stringent.
- States with Prohibition:
In states like Idaho, Kansas, South Carolina, and Wyoming, cannabis remains fully illegal. These states enforce strict anti-cannabis laws and do not permit any form of legalization, reflecting significant local resistance to cannabis reform.
Conclusion
The legal status of cannabis in the United States remains a patchwork of varying state laws and regulations. With public opinion increasingly in favor of legalization, and more states considering changes to their cannabis policies, this legal landscape is expected to continue evolving. For consumers, businesses, and policymakers, staying informed about the nuances of each state’s cannabis laws is essential for navigating this rapidly changing industry.